|
|
|
Purchase Hard Copy |
Section 4.9
Example Problem 4.1
The example problems presented in this section refer to a spreadsheet solution. Click on the link below to get the file:
Chapter 4: Excel Spreadsheet Solutions
Given: A lap splice is connected with (11) A325-X bolts as shown in Figure 4.9.1.1. Assume that the applied load consists of 40% dead load and 60% live load. The steel plates are ASTM A36 steel, the bolts are fully pretensioned 3/4" diameter ASTM A325-X bolts in standard holes. The faying surface is class A. No fillers are used.
Figure 4.9.1.1
Lap Splice
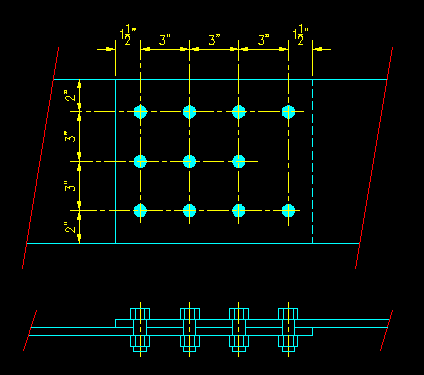
Wanted: Determine the capacity of the connection based on bolt strength as specified below. Consider both LRFD and ASD. Express your results in terms of service load levels.
- Determine the slip capacity of the connection.
- Determine the bearing capacity of the connection.
Solution:
Since the load combination only includes live and dead load, ASCE 7 load combination 2 (for both LRFD and ASD) will be the controlling case. The relationship between factored and unfactored load is:
Pu = 1.2D +1.6L = 1.2(0.40Ps,eq) + 1.6(0.60Ps,eq) = 1.44 Ps,eq
The ASD case is simply the D + L:
Pa = D +L = (0.40Ps,eq) + (0.60Ps,eq) = 1.0 Ps,eq
a) Slip Capacity - (See SCM J3.9)
rn = mDuhfTbns = 9.49 kips/per bolt
where: m = 0.30, Du = 1.13, hf = 1.00, Tb = 28 k (from Table J3.1), and ns = 1 (each bolt has only 1 shear plane).
The connection has 11 bolts, so, for the connection:
Rn = (9.49 k/bolt)(11 bolts) = 104 kips/connection
For LRFD, the capacity is determined by:
Pu = 1.44 Ps,eq < fRn = 1.0(104 kips/connection) = 104 kips/connection
Ps,eq < 72.5 k/connection (LRFD)
For ASD, the capacity is determined by:
Pa = 1.0 Ps,eq < Rn/W = (104 kips/connection)/1.5
Ps,eq < 69.6 k/connection (ASD)
Observations:
- In this case, LRFD allows more load than ASD. This is because the DL is more than 25% of the total load.
- These numbers are NOT the ACTUAL theoretical slip forces. These are the values that the specification allows to guarantee that slip will not occur.
b) Bearing Capacity - (See SCM J3.7)
The nominal capacity of a single shear plane is computed by:
rn = FnAb = 30.0 kips/shear plane
Where Fn = 68 ksi (from SCM Table J3.2) and Ab = .4418 in2 (area of a 3/4" diameter circle).
The connection has 11 bolts, all in single shear, so, for the connection:
Rn = (30.0 k/shear plane)(11 shear planes) = 330 kips/connection
For LRFD, the capacity is determined by:
Pu = 1.44 Ps,eq < fRn = 0.75 (330 kips/connection) = 248 kips/connection
Ps,eq < 172 k/connection (LRFD)
For ASD, the capacity is determined by:
Pa = 1.0 Ps,eq < Rn/W = (330 kips/connection)/2.0 = 165 kips/connection
Ps,eq < 165 k/connection (ASD)
Observations:
- In this case, LRFD allows more load than ASD, again because the DL is more than 25% of the total load.
- The resulting values are loads that can be safely carried without causing shear failure in the bolts.
Solution Summary
The following values are the capacities of the CONNECTION based on two bolt limit states. The total capacity of the connection is also a function of the capacity of members in the connection.
| LRFD | ASD | ||||
| Limit State | fRn | Ps,eq | Rn/W | Ps,eq | |
| (k) | (k) | (k) | (k) | ||
| Slip | 104 | 72.5 | 69.6 | 69.6 | |
| Shear Rupture | 248 | 172 | 165 | 165 | |
| Answer | Answer | ||||
Observations:
- Notice that the bearing values are larger the slip values. This is to be expected. Slip will occur before the bolts fail in shear. The load level that you want the connection to carry will depend on whether or not you want to allow slip to occur in your connection.